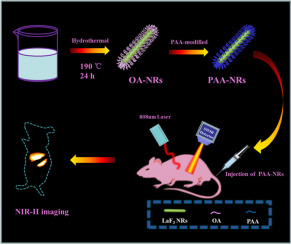
Molecular imaging is transforming the way researchers understand, diagnose, and treat cancer. At Electro-Molecular Discovery (EMD Bio), we are at the forefront of this revolution, offering high-resolution imaging probes tailored for cancer research applications including tumor biomarker detection, hypoxia mapping, angiogenesis imaging, and targeted drug delivery tracking.
z
h
What is Molecular Imaging in Oncology ?
Molecular imaging involves the non-invasive visualization of biological processes at the molecular and cellular levels within intact living organisms. Unlike conventional imaging methods, molecular imaging uses targeted probes to report on specific tumor-related activities, such as receptor expression, metabolic pathways, and cellular responses to treatment.
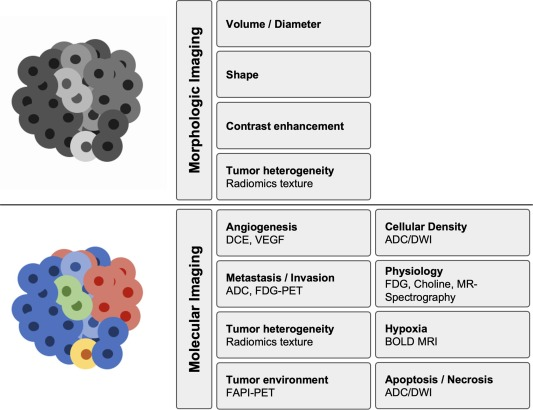
Applications in Cancer Research
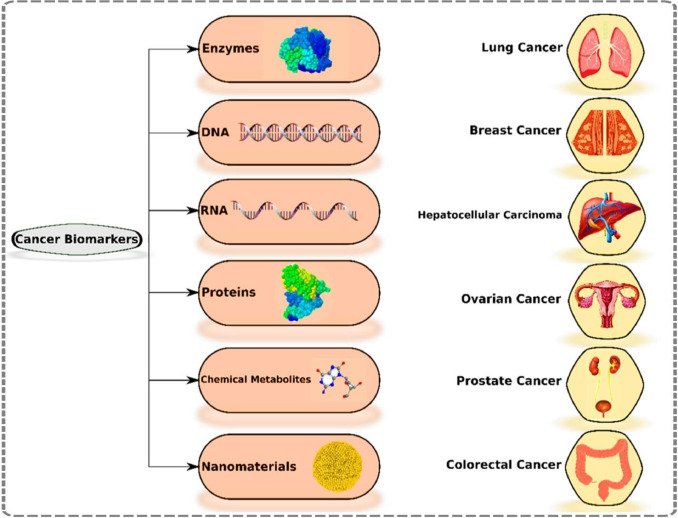
- Tumor Biomarker Detection
Detect overexpressed proteins (e.g., HER2, EGFR, PSMA) using fluorescent, radiolabeled, or bioluminescent probes. These tools provide unparalleled sensitivity for real-time cancer biomarker imaging, enabling earlier and more accurate tumor detection.
Learn more : here
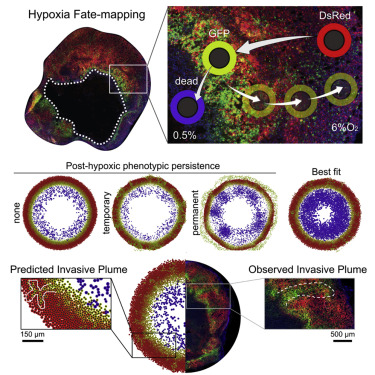
- Hypoxia Mapping
Visualize regions of low oxygen tension, a hallmark of aggressive tumors, using specialized probes such as nitroimidazole derivatives or NIR dyes. Hypoxia imaging guides therapeutic planning and predicts resistance to radiation therapy.
Reference : here
- Angiogenesis Imaging
Monitor the formation of new blood vessels using probes that target VEGF, integrins, or CD105. Angiogenesis imaging provides insights into tumor growth dynamics and response to anti-angiogenic drugs.
See NIH resource : here
- Dr ug Delivery Tracking
Track the biodistribution of therapeutic agents with PET, SPECT, or optical tracers conjugated to drugs, nanoparticles, or antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). This enhances the development of personalized treatments.
Read : here
Imaging Modalities Supported
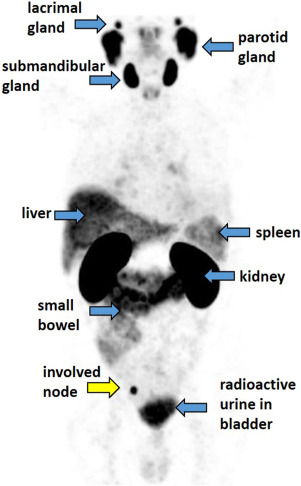
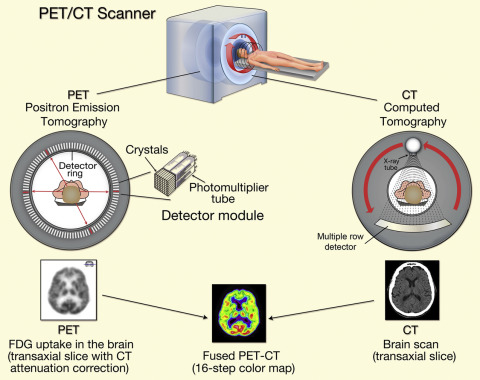
- PET/CT Imaging (Positron Emission Tomography) : High sensitivity for radiolabeled tracers such as 18F-FDG, 64Cu, or 89Zr.
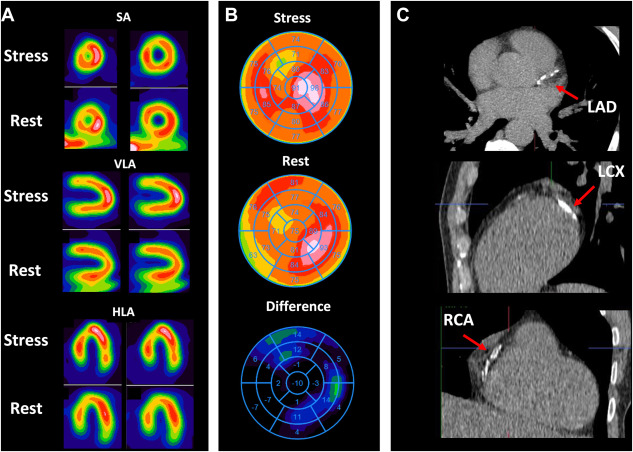
- SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) : Cost-effective radionuclide imaging with gamma-emitting isotopes.
- Optical Imaging (Fluorescence & Bioluminescence) : Ideal for in vivo small animal models, using far-red or NIR dyes.